Spiders belong to the Phylum Arthropoda, invertebrates with segmented bodies and jointed limbs. Their bodies consist of two segments, the cephalothorax (prosoma) and the abdomen (opistosoma). The cephalothorax seperates them from insects where the head and thorax are seperate segments. The cephalothorax and the abdomen are connected by the pedicel.
More detailed information can be found here.
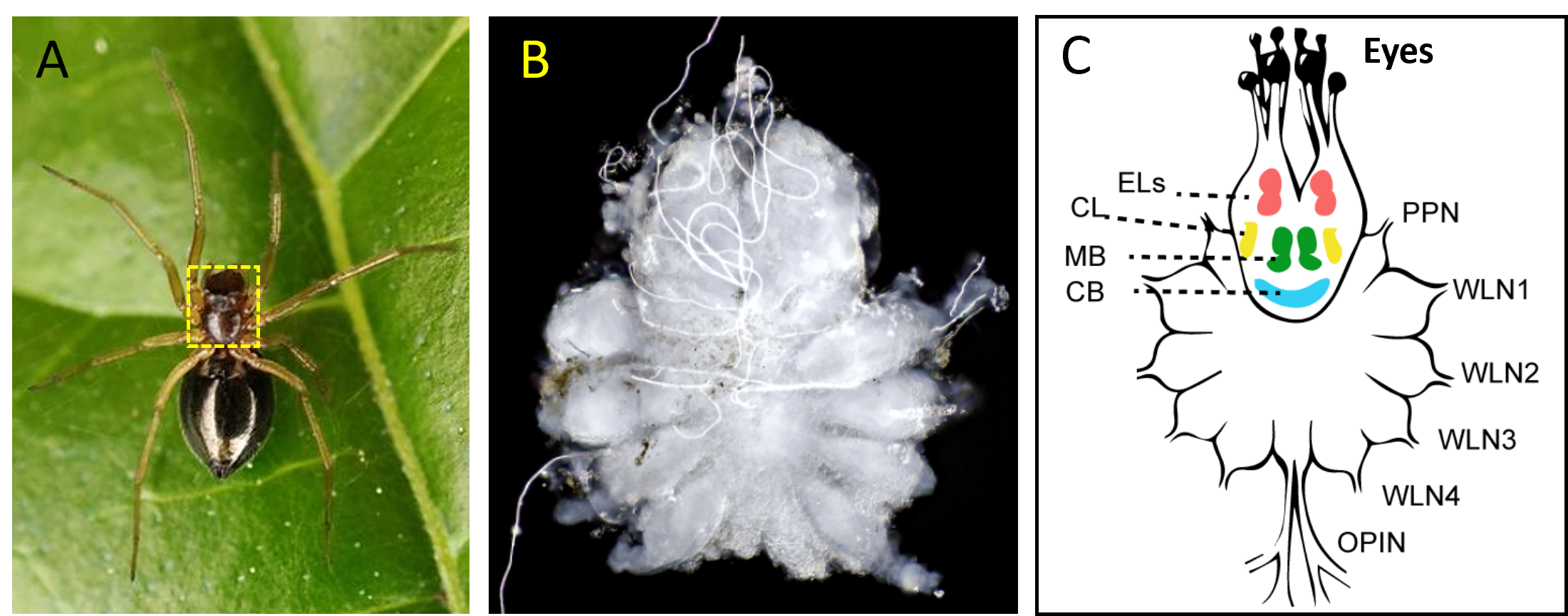
A: Photo by Justin Jacobs. CC_BY_4.0. B/C: Credits: Jin et al., 2023. CC_BY_4.0
A: Photograph of an adult male Hylyphantes graminicola. In yellow the cephalothorax that holds the brain (B)
B: Dissected brain of the spider Hylyphantes graminicola
C: Schematic diagram of the organization and major structure of the spider CNS in dorsal view.
Hinke Boer, Fons Brauers, Andy Louter, Lindsey Pennaertz, Aisha Raja and Tonny Mulder - University of Amsterdam