Brains of this world: Prefrontal cortex
By Andy Louter
_animation.gif)
By Andy Louter
_animation.gif)
There is no universally accepted definition of the prefrontal cortex, but it is regarded as the cortex region that receives inputs from the thalamus. The prefrontal cortex saw significant expansion in primates this is most likely due to the increased sensory areas in primates. Behavior is a key component of the function of the prefrontal cortex. The specific behaviors this affects vary from species to species, but there are general behavioral capacities that are common in mammals. The prefrontal cortex supports cognitive function and is thereby directly involved in the temporal organization of behavior; an example of this is social behavior.
The Orbital frontal cortex(OFC) has important functions to support the higher cognitive functions of the PFC. For instance it plays a crusical part in the evluation an response of reward value same as the LPFC. Also it exibits a function where it uses the sensory input with the rewards to make decisions. What the OFC is also used for is emotional responses it interperets the emotional stimuli and generated responses. The OFC is also very important in impuls controle it inhibites impulsive resonses if for instance the OFC is damaged this will lead to impulsivity and diffeculty in following social norms. For this reason the OFC also has a role in the understandence of social interactions it is the main proccesing area for social norms and behavior. The OFC also has a function in the intergration of sensory information it asseses its rewarded value especially in taste where the OFC contributes in flavor perception and complex food preferences. Learning and memory are also functions of the OFC where it is especially contributing in the bavior based on new experiences and to learn from them. It helpt to adapt behavior when the rules or exepted outcomes change. Suggested it also that the OFC contributes in the proccesing of pain both physical and mental (Rolls et al, 2004)
The ventral medial Prefrontal cortex(vmPFC) is anatomically located in the areas 11, 12, 25, parts of 32 and the lower medial portion of 10 of the Brodmann areas. Functions of this regions can be derived form the study of lesions. Theres lesions can arise from different causes like tumors,strokes or traumatic brain injuries. In the study there was looked at brains with lesions in the vmPFC were there was seen that the patients showed differences in functions. Personality changes, decision-making, emotional expressions, social cognition and memory where things that changed. Thourgh this it can be said that these functions are in a un damaged situation the normal functions of the vmPFC. The more specific functions are that the vmPFC is especially responsible for the things as descision-making, finecial planning, emotional responses, emotional interpetation of others and the intergration of memory and context. When the vmPFC is damaged patients show personality changes and lack of empathy and also the earlier staded functions are not working normally. The view the artikel provides is that the vmPFC is a important subarea where especially the emotional evaluation is carried out and if damaged leads to personalty changes (Schneider et al, 2017).
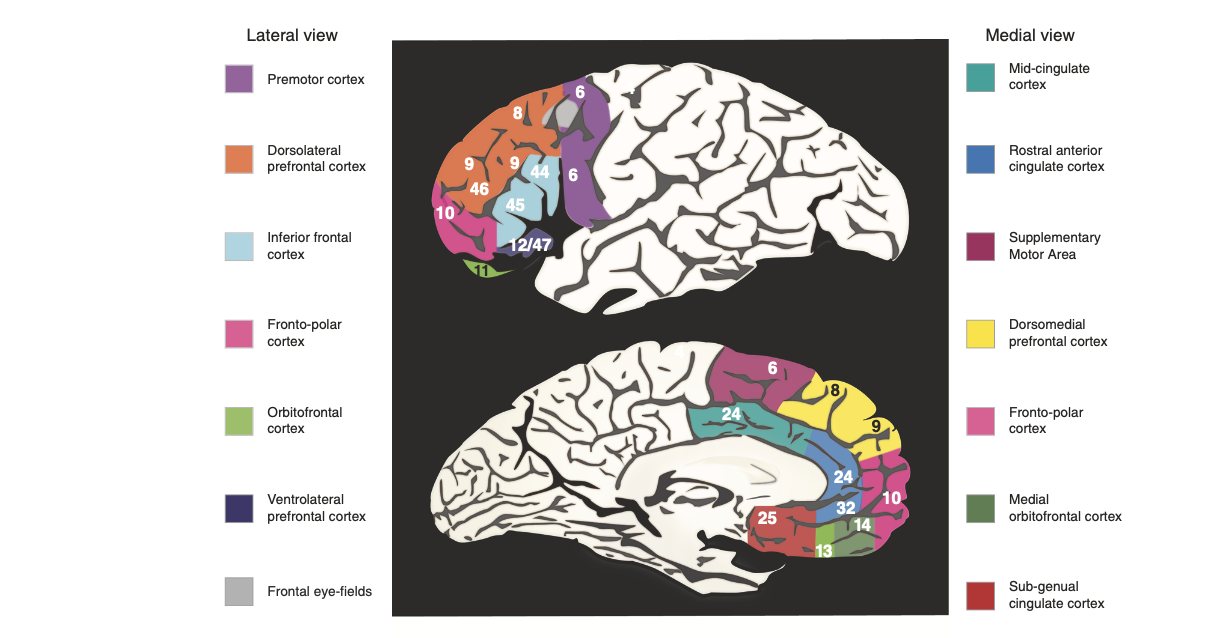
Important regions of the PFC with brodmann area numbers; Credits: Friedman and Robbins, 2021; CC_BY_4.0
The lateral prefrontal cortex(lPFC) is a sub region of the prefrontal cortex it is located on the lateral side of the frontal lobe. This region is involved in multiple cognitive functions such as reward evaluation, intergration of multiple piece information, valuation of continuing for higher reward or stopping, abstract concepts valuation and evaluating between different actions and there outcomes. The LPFC has a representation of both cognitive and value based infromation and even that value information is directly represented by the lPFC (Dixon et al, 2014). The lPFC has a strong input reception from the OFC a other prefrontal cortex subregion this connection is coming especially from the rostal area 11. This pathway may be the supllier iof objet outcome associations to the LPFC (Dixon et al, 2014). These anatomical connections suggest that the lPFC has the abbility to represent both cognitive and motivational information (Dixon et al, 2014).
The prefrontal cortex has next to the prior named regions and there corresponding functions also the region for language. This region is located in brodmann areas 44/45 these are located on the lateral side of the left hemishere(Teffer et al, 2012). The region is better known as the region of Broca. Broca is responsible for the spoken language. There are two types of spoken language syntax where it goes about structure like word order and sematics where the meaning of wordt is the main task. The 2 regions of broca are both resposible for one of the two functions. Region 44 of brodmann is mostly responible for for syntax and region 45 of brodmann for sematics (Goucha et al, 2015).
Hinke Boer, Fons Brauers, Andy Louter, Lindsey Pennaertz, Aisha Raja and Tonny Mulder - University of Amsterdam