Brains of this world: Amygdala
By Hinke Boer
By Hinke Boer

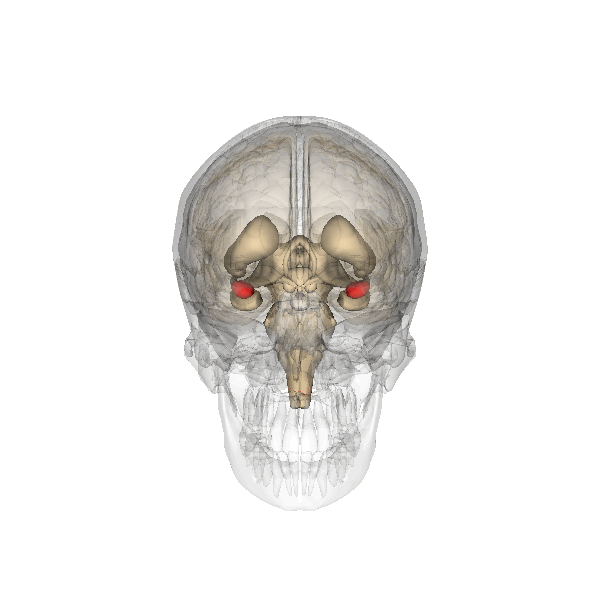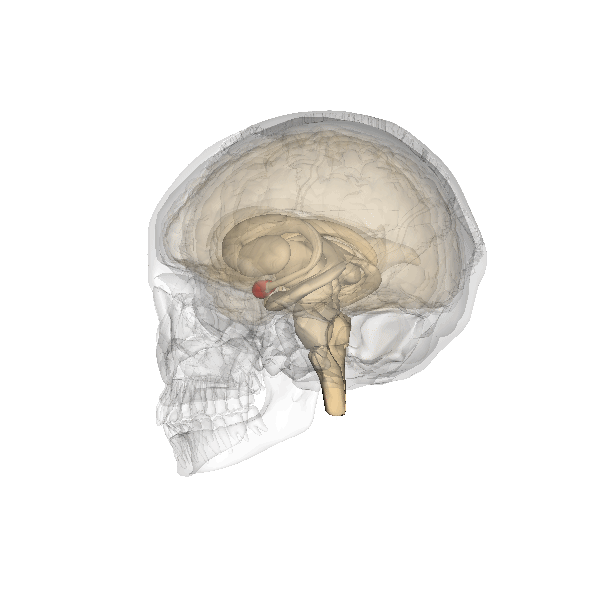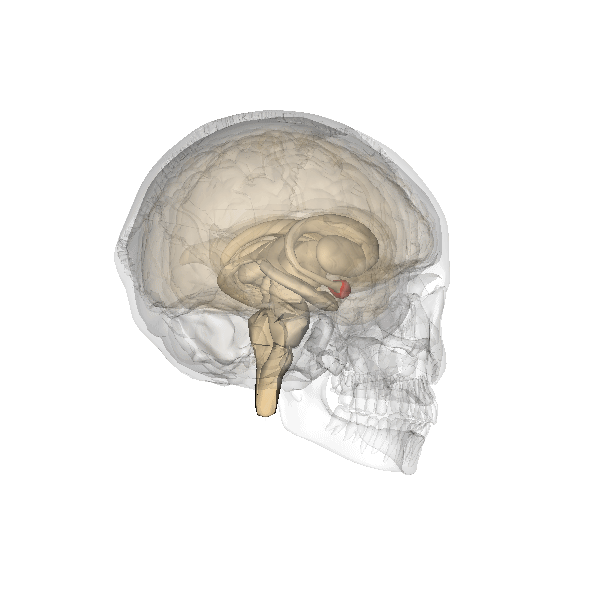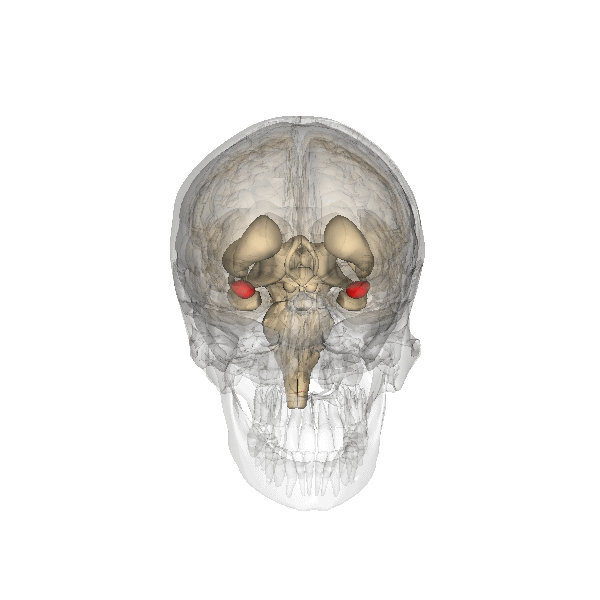
The amygdala is part of the limbic system and plays a vital role in the brain by overseeing three primary functions: the expression of emotions, memory processing and regulation of stimulatory input. The amygdala is situated in the medial temporal lobe with one in each hemisphere, positioned directly in front of the hippocampus.
The nuclei of the amygdala are categorized into three groups; the basolateral amygdala group (BLA), which include the lateral nucleus (LA), the basal nucleus (BA), and the basomedial nucleus (BM). The cortical group, comprising the nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract and cortical nuclei. And the centromedial group, consisting of the medial and central nucle.
There are 4 nuclei associated with fear conditioning circuit. The lateral, basal, basomedial and central nucleus. The lateral nucleus receives information about the external environment from the sensory thalamus and sensory cortices. The lateral nucleus reaches the central nucleus directly and via the basal nucleus and basomedial/accessory basal nucleus nucleus (Sah et al., 2003). Pathways from central nucleus to downstream ares then control defensive behavior and autonimc and endocrine responses (Johansen et al., 2011). Lesions of the CeA block the expression of fear conditioned response using visual or auditory CS (Sah et al., 2003).
Hinke Boer, Fons Brauers, Andy Louter, Lindsey Pennaertz, Aisha Raja and Tonny Mulder - University of Amsterdam